Predictive Models for Heart Disease Diagnosis
Health Care/Data Mining/Logistic Regression/Data Visualization/Machine Learning/
End-to-end ML pipeline on BRFSS 2020: data understanding & preprocessing, model selection (Decision Tree, Logistic Regression, KNN, Naïve Bayes), 10-fold CV, and cost-sensitive decision thresholding (FN » FP) tailored to healthcare risk.
Contents
Executive Summary
Tech Stack
Python NumPy Pandas scikit-learn Matplotlib SeabornData Preparation
- Target:
_MICHD(CHD/MI ever; map 2→0). - Cleaning: drop vars >90% null; handle special codes (7/9/77/98/99/777/999); min-max scale numeric; one-hot encode categoricals.
- Split: 60/40 train/test,
random_state=42, stratified.
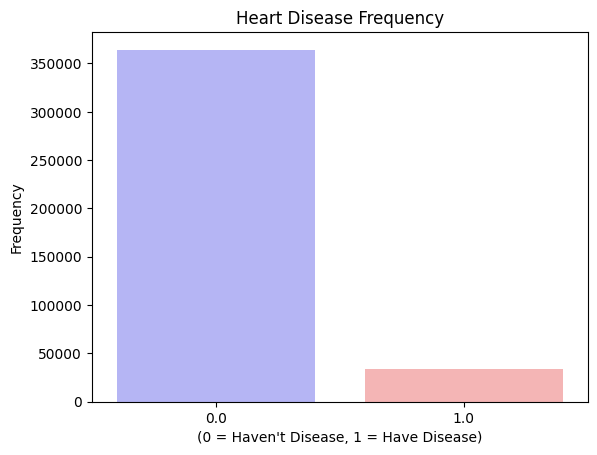
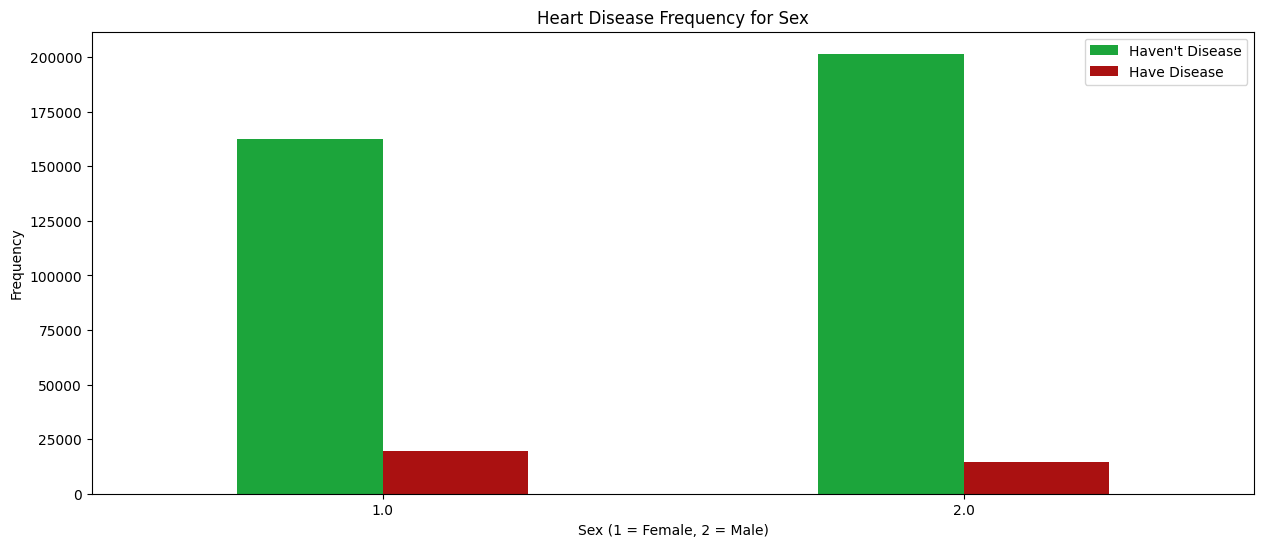
Modeling & Tuning
Compare Decision Tree, Logistic Regression, KNN, and Naïve Bayes. Hyperparameters via 10-fold CV with recall emphasis (KNN uses accuracy to avoid k=1 overfit).
- Decision Tree: tune
max_depth,max_leaf_nodes. - Logistic Regression:
penalty='l1',solver='saga',max_iter=2000, grid overC. - KNN: grid over
n_neighbors; best aroundk=8. - Naïve Bayes: Gaussian / Bernoulli based on encoding.
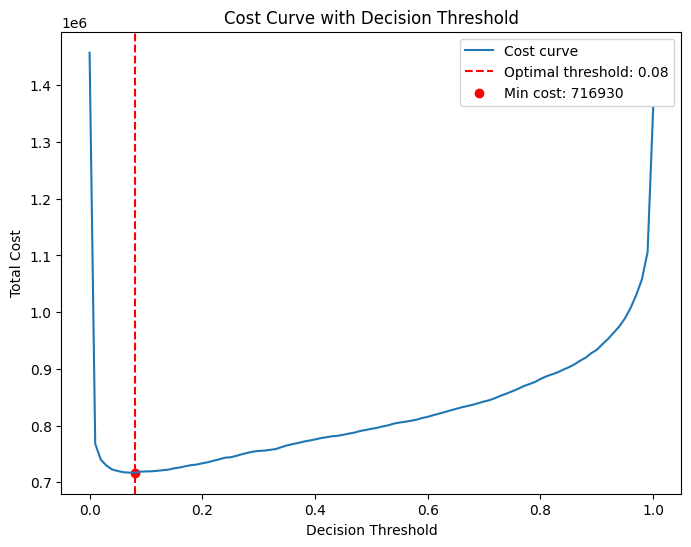
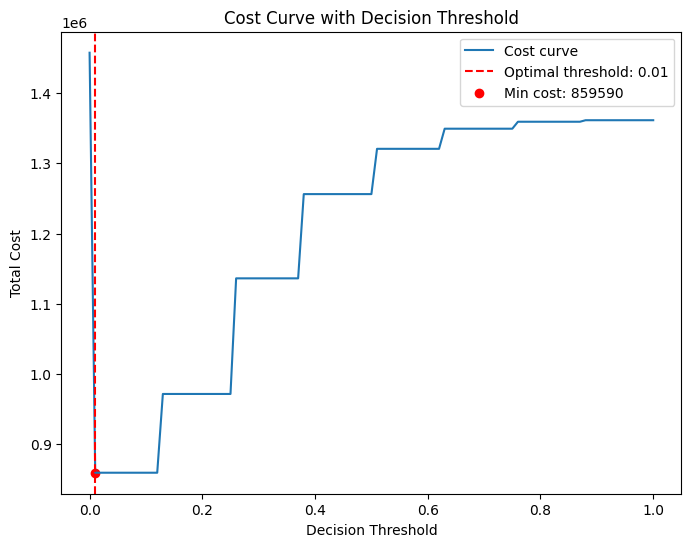
Cost-Sensitive Thresholding
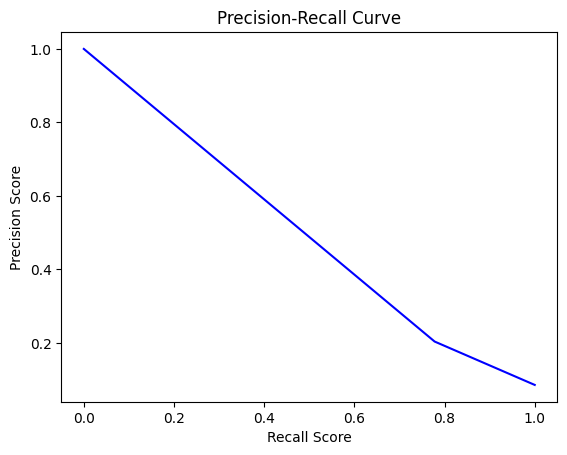
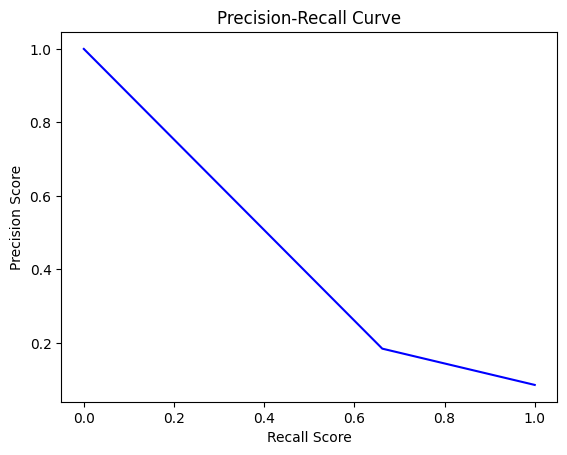
Total cost = 100×FN + 10×FP. Scan thresholds over [0,1] and select the minimum-cost point. Optimal thresholds used: DT=0.09, LR=0.08, NB=0.08, KNN=0.01.
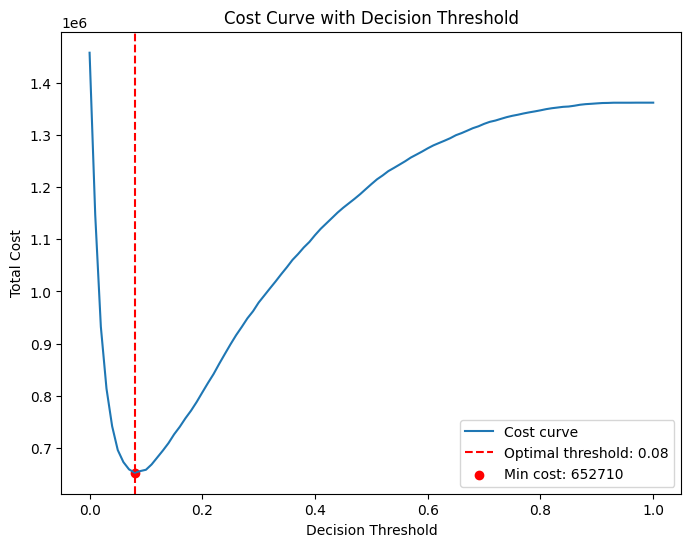
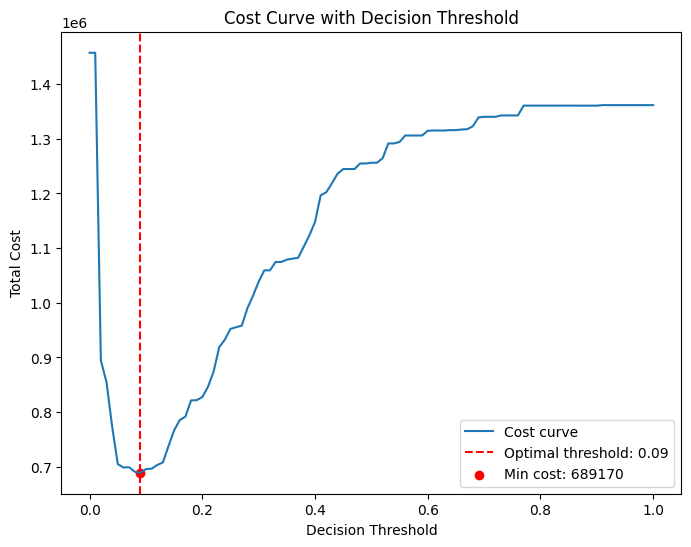
Evaluation
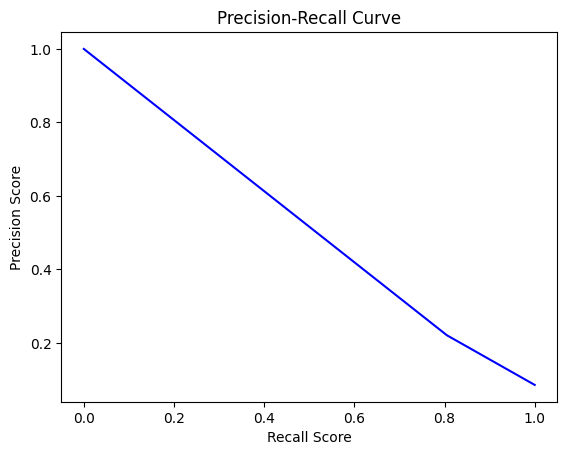
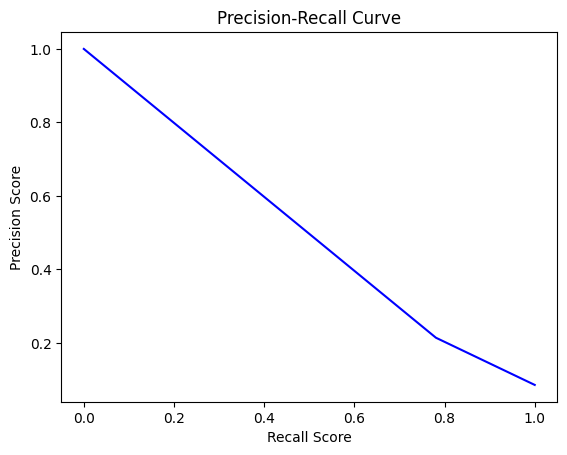
Report Accuracy, Precision, Recall, MAE, and Confusion Matrix before/after thresholding. Post-threshold, LR achieves the highest recall and lowest total cost.
| Model | Opt. Threshold | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 0.08 | Best recall & lowest cost after tuning. |
| Decision Tree | 0.09 | Competitive recall with tuning. |
| Naïve Bayes | 0.08 | High baseline recall; cost improved. |
| KNN (k=8) | 0.01 | Low threshold needed; recall trails LR. |
Selected Code
Train/Test Split & Target
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
y = df["_MICHD"].replace({2: 0}) # 1 = CHD/MI ever; 0 = otherwise
X = df.drop(columns=["_MICHD"])
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.40, random_state=42, stratify=y
)Recall-Focused CV & Threshold Search
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
import numpy as np
# Logistic Regression (recall-first)
lr = LogisticRegression(penalty="l1", solver="saga", max_iter=2000)
grid = {"C": [0.5, 1, 1.4142, 2, 3]}
lr_cv = GridSearchCV(lr, grid, scoring="recall", cv=10, n_jobs=-1).fit(X_train, y_train)
lr_best = lr_cv.best_estimator_.fit(X_train, y_train)
def min_cost_threshold(y_true, proba, fn_cost=100, fp_cost=10):
best_t, best_c = 0.5, float("inf")
for t in np.linspace(0, 1, 501):
yhat = (proba >= t).astype(int)
fp = ((yhat==1) & (y_true==0)).sum()
fn = ((yhat==0) & (y_true==1)).sum()
c = fn_cost*fn + fp_cost*fp
if c < best_c: best_t, best_c = t, c
return best_t, best_c
t_opt, _ = min_cost_threshold(y_test.values, lr_best.predict_proba(X_test)[:,1])Conclusion & Future Work
Cost-aware thresholding aligns the model with clinical priorities (catch more positives). Logistic Regression performed best after tuning. Next: calibrate probabilities, explore cost-sensitive learners and class-imbalance remedies, and validate on external cohorts.